Professional Services
Whether your challenge can be solved by our existing products or requires the development of new analytics solutions and market design approaches, our team is ready to help.
Optimizing Planned Outages at Elia: Successes & Lessons


What is outage planning, and why is it becoming a challenge for System Operators?
Outage planning is a critical process that involves scheduling outages on grid elements for maintenance, repairs, or upgrades. At Elia, the Belgian Transmission System Operator, the outage planning activity is a crucial task to further reinforce the electricity grid and ensure smooth operation while maintaining a consistent power supply to end-users. Based on the need for increased planning optimization, Elia Transmission Belgium embarked on a journey to integrate optimization strategies into its outage planning processes, supported by N-SIDE.
From this collaboration, a state-of-the-art outage planning optimization software solution was developed and integrated into Elia’s production systems, marking a significant milestone.
After the go-live of the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in 2021, a research and development initiative was launched, aiming to reinforce Elia’s outage planning optimization capabilities. Significant strides were made through rigorous exploration across fourteen research tracks. Four of them transitioned into industrial applications, while three others are currently on the verge of industrialization. Meanwhile, five tracks are currently on standby, awaiting further developments. As it can be expected in every R&D initiative, two tracks were halted due to insufficient convincing evidence of their feasibility and added value for the business.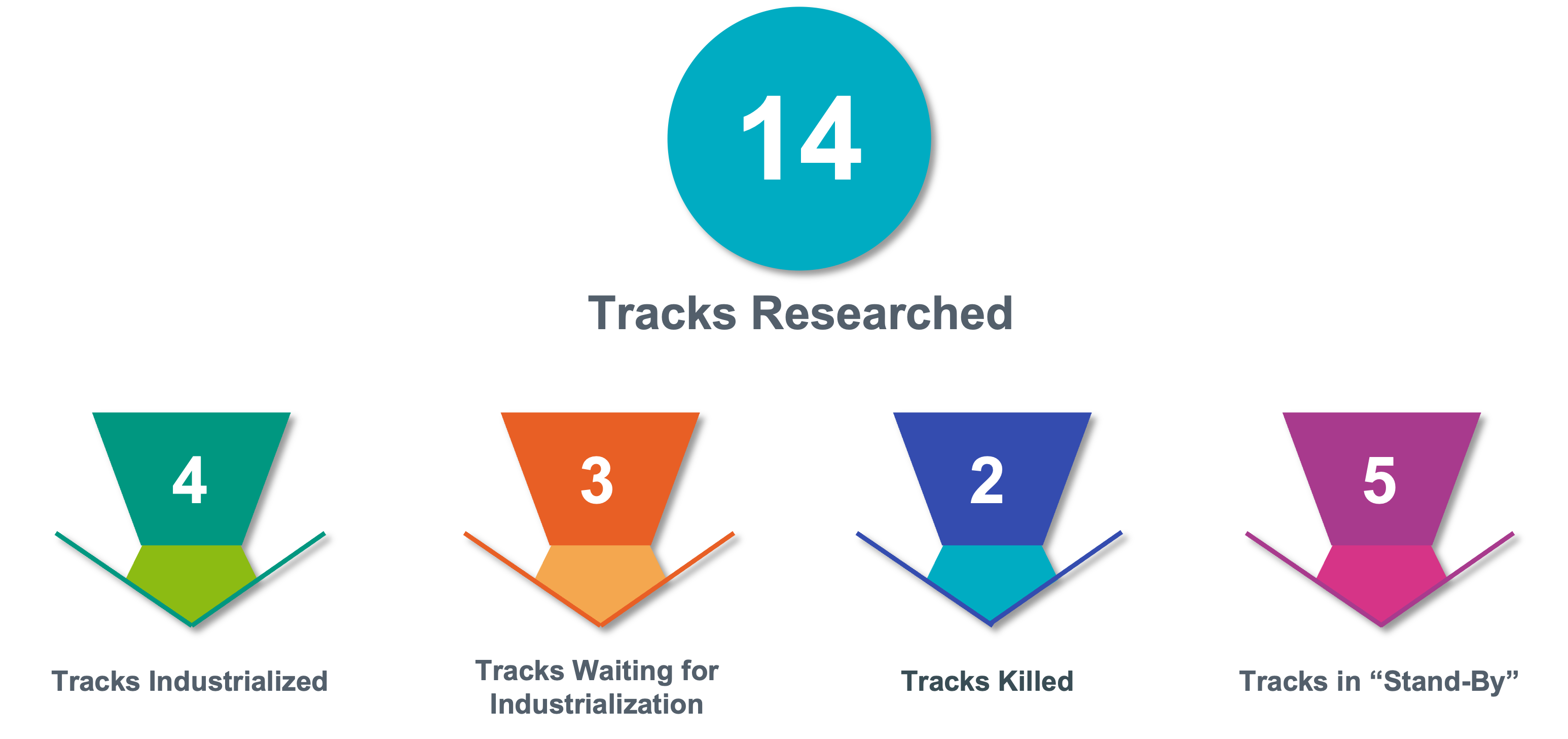
The collaboration between Elia and N-SIDE stands as a proof of the transformative potential of innovative solutions in the energy sector. This collaboration emphasizes the importance of adaptive and forward-thinking strategies in an ever-evolving energy landscape.
"Outage management is becoming more and more complex with Elia operating the high voltage grid in the interest of society. Human and artificial intelligence need to reinforce each other in order to be able to optimize our outages for maintaining and extending our grid. We relied heavily on the competences of N-SIDE to help introduce OPSO (outage planning optimizer) in our company."
Bart De Jong, Head of Network & Data Operations, Elia
Elia’s evolution with regard to outage planning
The catalysts for change
Over the recent years, Elia has made significant efforts to integrate renewable energy sources and evolve towards a more sustainable energy future. This transition poses important challenges for outage planning, requiring dynamic and flexible strategies to maintain grid security amidst the fluctuating behavior of renewable energy.
Moreover, there is a growing number of infrastructure projects carried out each year to cope, amongst others, with the integration of distributed energy sources and further development of the grid. All these interventions often require planned outages for safety reasons, therefore reducing the possibilities to perform other works.
Considering these challenges, Elia proactively embraced innovative technologies to enhance its outage planning processes.
For more details about the selected optimization technology and its usage in operations, a summary of the topic is provided in the following article: An integrated approach for the scheduling of grid activities requiring outages.
Why Elia chose N-SIDE to develop their decision-support outage planning optimization software
Elia’s decision to collaborate with N-SIDE to build up its outage planning optimization software comes with different reasons. First, N-SIDE is a software company that combines deep expertise in analytics, software development, and energy business to provide AI software solutions, from system planning to the control room of the future. Another strong asset of N-SIDE is that it can accompany its customer at all stages of the solution: incubation, industrialization, and continuous improvement, along with support & maintenance.
The R&D odyssey: pioneering the future of outage planning
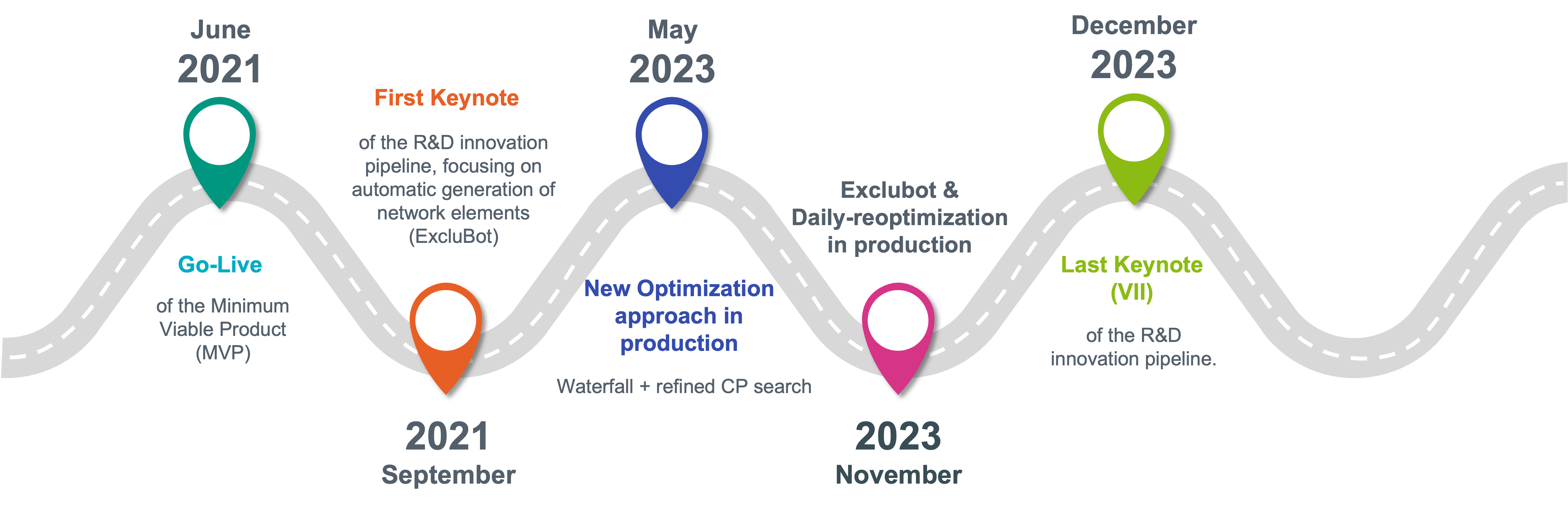
The first production release of the outage planning optimization software (OPSO) occurred in June 2021. While the planning solutions initially provided by OPSO were acceptable for the business, opportunities to further optimize the outage planning and align it with the existing way of working were quickly identified. Consequently, recognizing the need for enhancement, a parallel joint R&D program was initiated between N-SIDE and Elia in order to identify opportunities to further extend its capabilities while ensuring continuous improvement.
Agile innovation: driving R&D success together
The R&D framework, initiated in July 2021 following the production release and concluded at the end of 2023, represented a collaborative effort between the N-SIDE and Elia teams. From N-SIDE, the consulting team comprised an optimization expert, a software engineer, a data engineer, and a power system expert, demonstrating a robust combination of business, technical, and analytical expertise. The Elia group side was spearheaded by an operational planning engineer, who assumed the role of Project Manager alongside a Business Sponsor, a Business Analyst, and a Program Manager. This structure was reinforced by the occasional inclusion of planners and analysts, who provided essential business support through input requirements and result validation.
Key to the success of this initiative was the adoption of an Agile methodology, which infused the project with a dynamic and adaptive approach. This methodology facilitated a synergy between the teams, allowing for a continuous exchange of ideas and strategies and ensuring alignment with evolving business needs. Each R&D track was initiated with a comprehensive project plan that clearly outlined the business problem, scope of study, timeline, final objectives, expected milestones, evaluation criteria, and potential risks. This forward-thinking approach enabled the swift identification and discontinuation of underperforming tracks, thereby reallocating resources to those yielding high business value. The flexibility inherent in this method allowed for rapid adjustments and pivots in response to new insights, ensuring the prioritization of the most promising tracks.
Understanding the need for research and development
The primary goal of this R&D journey was to support future improvements and extensions associated with OPSO. In particular, a couple of improvement opportunities associated with the solver were identified:
- Improvement of the optimization speed of the Constraint Programming (CP) solver algorithm, such as:
- Leveraging decomposition methods to divide the problem into individual sub-problems;
- Improving the outage grouping behavior of the CP by enhancing the heuristics behind the search;
- Boosting the optimization process by learning from previous runs;
- Improvement of existing features in the CP solver, such as :
- Reducing the complexity of the problem by simplifying the expression of network constraints or non-working days;
- Improving the comprehension around scheduling choices made by the solver through the development of an explainability module;
- Addition of new features associated with the CP solver, such as:
- Implementing an optimality indicator (optimality gap);
- Developing a topology graph analyzer that can automatically detect and generate network constraints;
- Implementing the possibility to consider mandatory works in the CP solver.
Journey highlights
Overcoming Optimization Challenges
Initially, the team found that generating a high-quality outage planning schedule through a one-shot optimization approach was a challenge. This obstacle was transformed into an opportunity to innovate. Collaboratively, the teams studied an alternative strategy involving decomposition methods. This approach segmented the complex problem into manageable subproblems, each treated individually. This pivot not only resolved the initial issue but also led to a more efficient and effective optimization process while following the stage-like approach of operational planning used at Elia: first the planning of 400/220 kV grid, then lower voltages focusing first on critical works and filling the gaps with less urgent maintenances activities.
Addressing the Optimality Detection Dilemma
Another significant challenge was the difficulty in measuring how close the multitude of optimizations were to achieving optimality, a crucial metric for the Elia business. The collaborative effort led to the development of an optimality gap metric. It provides a reliable measure of proximity to the objective value, proving to be a valuable asset for the business as weekly monitoring of this metric provides a good overview of the optimization process’s health.
Enhancing Explainability in Outage Planning
The Elia teams aimed to get further insights into some scheduling choices made during the optimization process. This encompassed knowing when work could be planned, the impact of date changes, and reasons for scheduling infeasibilities. Addressing this challenge, the teams jointly developed an “Explainability Module.” This module moves away from the black-box nature of optimization processes by providing detailed insights for each work considered in the outage planning, answering all those critical questions. This development sparked unprecedented interest among the majority of Elia planners, who saw its potential to revolutionize the way they plan their grid activities.
Integrating Innovations for Operational Efficiency
Operational teams have the difficult task of manually generating and maintaining an extensive list of network constraints. The introduction of graph analysis algorithms for automatically generating these constraints significantly eased this burden. This innovation culminated in the industrialization of the ExcluBot solution, a breakthrough in the operational engineering process.
Adapting to Intra-Week Outage Planning Obsolescence
A challenge in operational planning was the rapid obsolescence of intra-week outage plans due to frequent changes occurring between weekend cycles. To address this, a new optimization framework was implemented to enable daily re-optimizations, facilitating intra-week updates of the optimized planning to incorporate the latest changes made by planners.
Key lessons learned for future industrialization of optimization tools
This collaboration allowed us not only to improve Elia’s outage planning capabilities but also to learn about the challenges and opportunities of implementing decision support software systems in the core operations of system operators. Throughout the whole journey, Elia and N-SIDE worked with a co-creation spirit, acting as ONE team. During the entire experience, we have gleaned several critical lessons, allowing us to continue improving the software and services that we provide to our customers.
Firstly, we learned the importance of involving the end-users as early as possible to foster a sense of participation and ownership. In a dynamic operational setting, every facet of new software will be constantly scrutinized and challenged by end-users, a process that persists well beyond the initial months of deployment. It’s imperative, in such conditions, as a software service provider to carefully listen to their feedback and rapidly respond in an adaptable manner to any issues of frustration or negative experiences they encounter with the tool.
Secondly, the significance of data quality for optimization software cannot be understated. When embracing such a technology, a Transmission System Operator must ensure to provide data that is up to date, complete, reliable, consistent and accurate. Without that, it is not possible for the solver to generate an acceptable solution.
Thirdly, we've recognized the substantial effort required to manage the organizational change prompted by integrating such software into operations. This effort demands considerable time and resources and should not be underestimated. To facilitate this transition effectively, it's critical to enhance the interpretability of the solver's decisions and provide comprehensive support to end-users. Neglecting this aspect risks diminishing enthusiasm and acceptance of the solution among stakeholders.


.jpg)
About the Author
Jérôme Bausier holds a Master’s Degree in Bioscience Engineering and a specialization in Data Science from UCLouvain (Belgium). As an Energy Analytics Consultant at N-SIDE, he made an important contribution to the success of this outage planning innovation pipeline. His role is to create innovative prototypes using advanced analytical techniques and transform them into scalable solutions for the Energy Sector, especially for Grid Operations.
Jérôme Bausier




Other content like this one...

Article
How the TSO Elia optimizes outage planning with Constraint Programming
Outage Planning is becoming increasingly complex for System Operators. Anticipating the challenges that come along with the full transition of the energy landscape is becoming crucial for System Operators to...
Read more-1-1.png)
Article
An integrated approach for the scheduling of grid activities requiring outages
To achieve a sustainable and resilient future, we’re going to have to learn to tackle unpredictability in the power grid — and that requires novel approaches to decision making. As energy systems become more complex...
Read more.jpg)
Article
N-SIDE develops a decision-support software product for congestion management in grid operations
Solving grid congestion is a continuous challenge for Transmission System Operators (TSOs), who are responsible for developing, maintaining, and operating the high-voltage electricity grid...
Read more









