Professional Services
Whether your challenge can be solved by our existing products or requires the development of new analytics solutions and market design approaches, our team is ready to help.
How can a DSO manage simultaneously grid planning, scheduled maintenance and congestion management via market solutions?


The EUniversal Portuguese demonstrator
This article is part of a broader series linked with the EUniversal Project and how N-SIDE is helping 3 major DSOs to simplify communications. You can find the first article introducing the global context here
The new local consumption and production patterns from residential consumers pose a significant challenge for DSOs in managing their power grid effectively. By relying on residential flexibility enabled through market approaches, a DSO can avoid costly reinforcements needed to handle peak demand, as well as congestion.
The EUniversal project proposes market solutions that rely on a common European standard (called UMEI) to communicate with multiple flexibility market platforms simultaneously. In this episode, we will focus on the concrete setup around the flexibility procurement of E-REDES, the main DSO in Portugal.
E-REDES challenges
As many other DSOs, E-REDES needs to create its long-term grid planning years ahead and plan maintenance while ensuring the fewest disturbance possible weeks ahead. Closer to real time, it prepares itself to avoid physical congestion and control voltage violations which are expected to become more and more frequent, not to mention phase balancing issues.
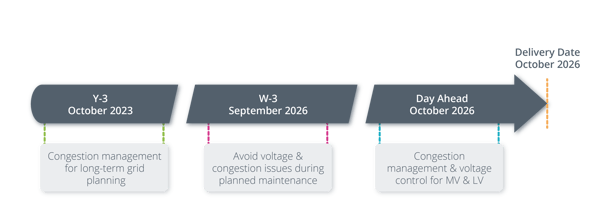
In Portugal, the purpose of the UMEI is to tackle the following problems through market mechanisms:
- Congestion management in Middle Voltage (MV) grids the day prior to when the problem would occur via a flexibility day-ahead market
- Integrated Voltage Control in MV and Low Voltage (LV) grids the day prior to real-time via a flexibility day-ahead market
- Contracting flexibility services weeks ahead to avoid voltage and/or congestion issues during planned maintenance action in MV grids
- Congestion Management years ahead for medium and long-term grid planning through market mechanisms, replacing grid reinforcement
Managing all these problems in parallel requires a good view on when market operations happen since they interfere with each other. Contracting flexibility 3 weeks ahead for planned maintenance could for example also help to solve a problem of voltage control closer to real time.
How the market works
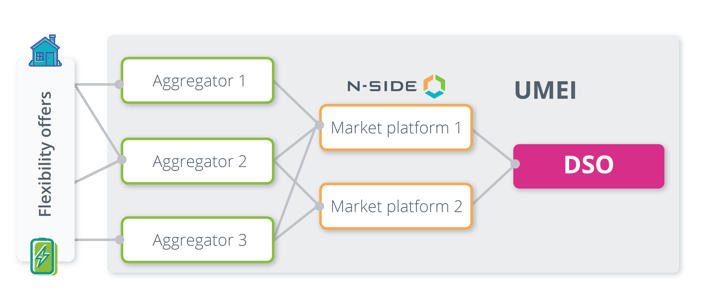
In this demonstrator, two Flexibility Market Platforms with distinct trading methodologies are being tested, each considering the operator’s market design and flexibility products and services. Their role is to ease the link between aggregators and DSO (i.e. E-REDES here) through an auction based mechanism. Visually-speaking, taking back the figure from the previous article, the overall setup looks like this
For flexibility to be procured, the different parties need to communicate. This is done in a series of phases, going from pre-qualification to trading phases. As described in Article 2 these phases define the structure of the UMEI.
Optimized market clearing with the N-SIDE Local Flexibility Market Platform
The N-SIDE Local Flexibility Market is one of the platforms running in Portugal. One of its strengths is its advanced market clearing mechanism that is based on advanced optimization models and algorithms. It can concentrate all the liquidity of the market with a closed-gate mechanism, before clearing it by maximising social welfare while respecting asset and network constraints. The output of the algorithm results in the optimal bid selection (i.e. that maximises social welfare) which has also one of the lowest procurement costs possibly achievable for the DSO. For more information on how modern power auctions work, you can read this blogpost
Modular market clearing and permanently adaptable network configuration - a unique innovation of this pilot, recognized by leading researchers in the field
On top of taking advantage of the classic features of the N-SIDE Power Matching Algorithm, the N-SIDE platform allows the use of an innovative concept called semi-dynamic flex zones to fit with E-REDES extra requirements.
In general, market platforms need detailed grid data to model the network. Once the network configuration is done, it can hardly be changed. The N-SIDE platform uses a more dynamic approach to model the flexibility zones that makes the tool more adaptable and decreases the level of detailed grid data needed.
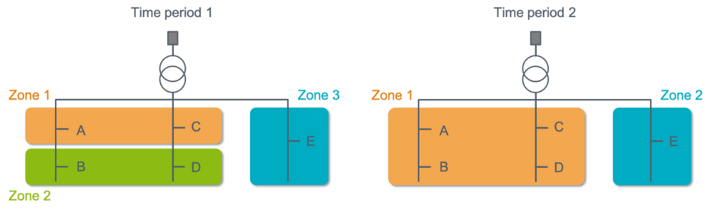
"Modelling semi-dynamic flex zones is not only very useful to E-REDES, it is also a unique feature that N-SIDE platform is currently able to support, allowing a more efficient and secure use of the flexibility available with limited network information"
Clara Gouveia, Area Manager and Senior Researcher in the operation of distribution networks within smart grid context at INESCTEC
Co-Author
Louise holds a Master degree in Applied Mathematics from UCLouvain (Belgium) during which she focused on machine learning and optimization. At N-SIDE she has contributed to multiple projects around energy markets and flexibility.
The Euniversal Series
The new local consumption and production patterns from residential consumers pose significant challenges for DSOs in managing their power grid. To avoid costly reinforcements in order to cope with very local issues, relying on residential flexibility is envisioned through market approaches.
The EUniversal project proposes to rely on a common standard at European level to ease market interactions. Adopting it will prevent an unstructured IT setup that leads to vendor lock-in, hindering flexibility and market competition before it is too late.
Through this series, learn more about the problem, how the solution was designed and how it is used by major DSOs in Europe.
- How N-SIDE helps DSOs take the most of various sources of flexibility simultaneously: the EUniversal project
- The UMEI - How a European standard is simplifying DSO interactions with local markets.
- How can a DSO manage simultaneously grid planning, scheduled maintenance and congestion management via market solutions?
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement No 864334.
This article reflects only the N-SIDE view. The European Commission Innovation and Networks Executive Agency is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains.



About the Author
Pierre is an Engineer and Economist active in market-oriented activities at N-SIDE. He has contributed to some Euphemia R&D achievements and to the deployment of our Power Matching Algorithm in India. He has also worked for system operators by designing and delivering solutions for local and balancing markets. Pierre is now the Product Manager of the N-SIDE Power Matching Algorithm, shaping how our market clearing offer can evolve to allow even more end-consumers worldwide to get access to cheaper and cleaner electricity.
Pierre Crucifix





Article
How N-SIDE helps DSOs take the most of various sources of flexibility simultaneously: the EUniversal Project
Together with grid operators, universities, research institutes, and market platform providers, we're building a standardized solution to enable multiple market platforms to work simultaneously with the EUniversal project, testing in three different European countries to ensure adaptability. read more
Article
The UMEI - How a European standard is simplifying DSO interactions with local markets.
read more











